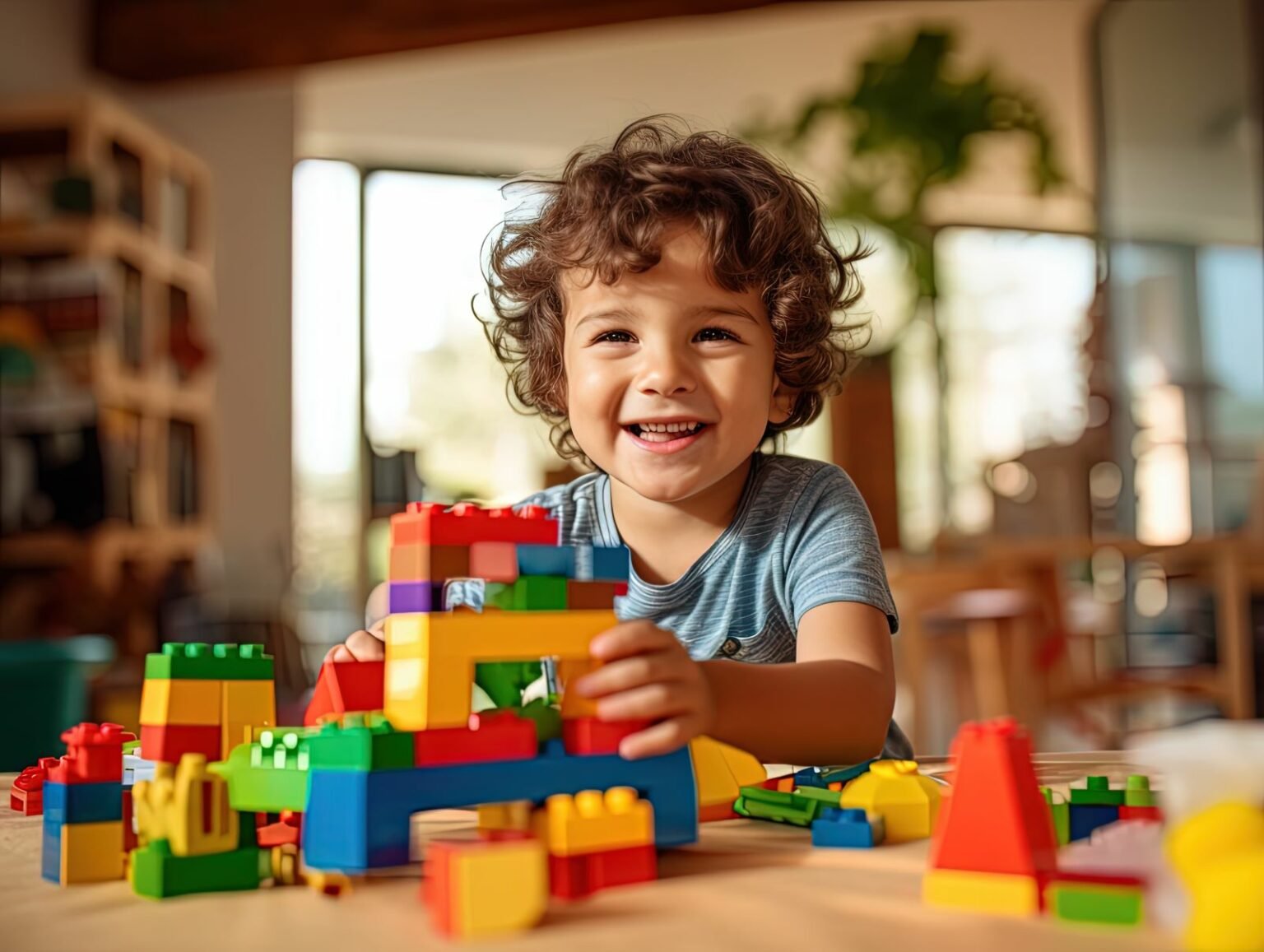
Play is not just a pastime for young children; it is a fundamental aspect of their development and learning journey. From building towers with blocks to pretending to be superheroes, play serves as a vital tool for fostering creativity, social skills, and cognitive development. Let’s delve into the significance of play in the early years:
Fostering Creativity:
1. Imaginative Play:
Through imaginative play, children explore their creativity by role-playing, pretending, and inventing new scenarios. Whether they’re playing house, creating elaborate storylines, or building forts, imaginative play encourages children to think outside the box and express themselves freely.
2. Artistic Expression:
Art activities such as drawing, painting, and sculpting provide children with opportunities to express their thoughts, feelings, and ideas in a visual medium. Engaging in artistic endeavors stimulates imagination, fine motor skills, and problem-solving abilities.
3. Exploratory Play:
Allowing children to explore their surroundings through sensory play, such as digging in sand, splashing in water, or squishing playdough, stimulates their senses and encourages curiosity. This hands-on exploration fosters creativity and lays the foundation for scientific inquiry and discovery.
Cultivating Social Skills:
1. Cooperative Play:
Playing with peers teaches children valuable social skills such as cooperation, communication, and compromise. Whether they’re collaborating on a building project or taking turns in a game, cooperative play promotes empathy, teamwork, and conflict resolution.
2. Role-Playing:
Role-playing activities, such as playing doctor, teacher, or firefighter, allow children to practice social roles and explore different perspectives. Through role-playing, children learn to understand and empathize with others, develop language skills, and negotiate social situations.
3. Building Relationships:
Play provides opportunities for children to form friendships, strengthen bonds, and develop a sense of belonging within their peer group. Shared play experiences create lasting memories and lay the groundwork for positive social interactions both inside and outside the classroom.
Enhancing Cognitive Development:
1. Problem-Solving:
Play presents children with challenges and puzzles to solve, whether it’s figuring out how to fit puzzle pieces together or building a structure that won’t topple over. These problem-solving experiences stimulate critical thinking, spatial awareness, and logical reasoning skills.
2. Language Development:
Play encourages language development through conversations, storytelling, and imaginative dialogue. Whether children are narrating their play scenarios, negotiating roles with peers, or describing their actions, they are actively building vocabulary, grammar, and communication skills.
3. Spatial Awareness and Math Skills:
Activities such as building with blocks, sorting objects, and playing with puzzles develop spatial awareness, geometric concepts, and early math skills. Through hands-on manipulation of objects and exploration of spatial relationships, children lay the groundwork for mathematical thinking and understanding.
Conclusion:
In the early years of childhood, play is not just a form of entertainment; it is a cornerstone of development. By fostering creativity, social skills, and cognitive growth, play lays the foundation for future learning and success. As parents and educators, we must recognize and value the importance of play in children’s lives, providing them with ample opportunities to explore, create, and imagine. Through play, children embark on a journey of discovery, growth, and joy, shaping the adults they will become.